Supervised ML: Titanic Survival
Environment
Python 3.8 with: Sklearn, Matplotlib, Seaborn, Graphviz, Pandas, Numpy, os
A conda environment for data science was created, and all of the programming was implemented in a Jupyter notebook. All of the associated files have been placed in my titanic repository on Github, and the README.md provides instructions for reproducing my results.
Introduction
The goal of this project was to predict whether 418 passengers on the Titanic survived given a similar dataset for 891 passengers. This was my first data science project using Python.
Findings
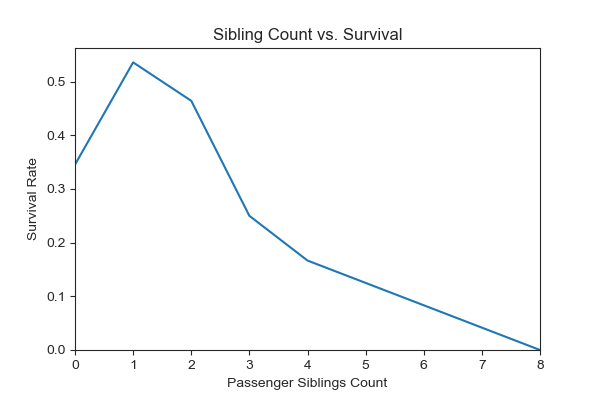
While exploring the data, the following graph revealed that the number of siblings a passenger had on board had a clear positive correlation with perishing.
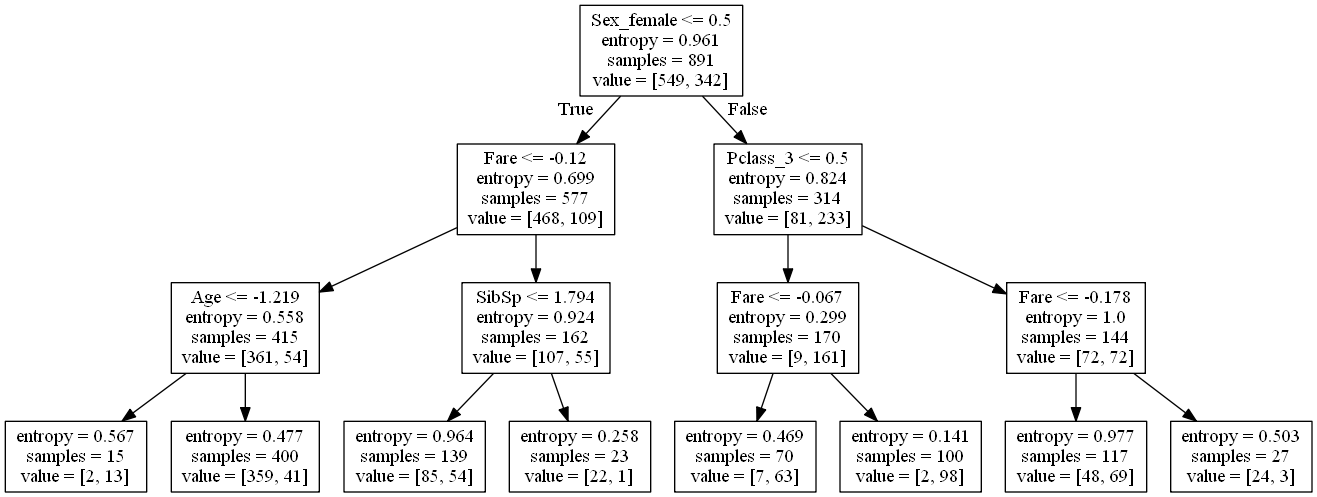
A decision tree was found to give good predictive results, with an accuracy score of 77.5% on the test.csv dataset.
Methodology Highlights
- Data Cleaning
- The name feature was divided into three features using regular expressions: Title, First Name, Last Name
- Missing values were imputed with the median value for numeric features or the most frequent value for categorical features
- Numeric features were transformed with standard scaling and categorical features were transformed via OneHotEncoder
- Exploratory Data Analysis
- Many plots were created to understand how aggregated groups faired relative to one another in terms of survival
- Modeling
- A decision tree classifier was applied, manually adjusting the max_depth parameter
- The default measure of impurity (Gini) gave unbalanced leaf nodes, therefore entropy was used instead
- 5 fold cross validation gave 81.6% mean accuracy on the train.csv dataset
- The graphviv library was used to plot the decision tree
- A random forest classifier consisting of decision trees was applied next, using random search to conduct hyperparameter tuning
- 5 fold cross validation gave 83.2% mean accuracy on the train.csv dataset
- Both the decision tree and random forest algorithms used the ROC AUC metric to guide decisions to avoid models that were overly biased by bias in the the train.csv survival rate

